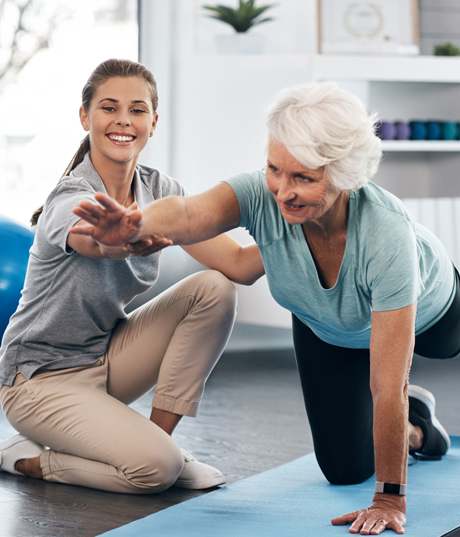

EXERCISE THERAPY
Exercise training or therapy can take many different forms. For some people it may be moving more and sitting less and for others it may mean getting on a bike, jogging or lifting weights. The ultimate goal is to use physical activity to improve health and wellbeing. Physical activity and physical fitness are known to be associated with achieving lifelong health and wellbeing.
Leading a more active lifestyle can influence many aspects of everyday life; from how much an individual socialises to their cardiac health and function. However maintaining a physically active lifestyle poses greater challenges when faced with neuromuscular diseases such as DM1.
Exercise therapy can be used not only to promote an active lifestyle but also to encourage a change in behaviour and improve quality of life.
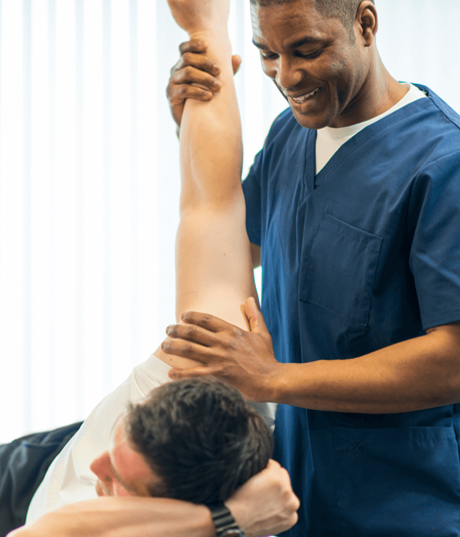

MANUAL THERAPY
Manual therapy is defined as the skilled passive movement of joints (joint mobilization/manipulation) and soft tissues (soft tissue mobilization/specific localized massage). Physicians focus mostly on osteokinematics, or gross motions of a limb (i.e., How far can this patient bend his/her knee?).
Manual physical therapists are concerned with normalizing arthrokinematics, or specific motions that take place between joint surfaces that allow for normal joint mobility (i.e., Why can’t this patient bend his/her knee? What specific joint movements or soft tissue restrictions are present?).
Manual therapists use specific hand placements and the precise application of forces to restore normal movement to joints and soft tissues. Manual therapy is used in conjunction with other physical therapy techniques, exercises, and modalities.
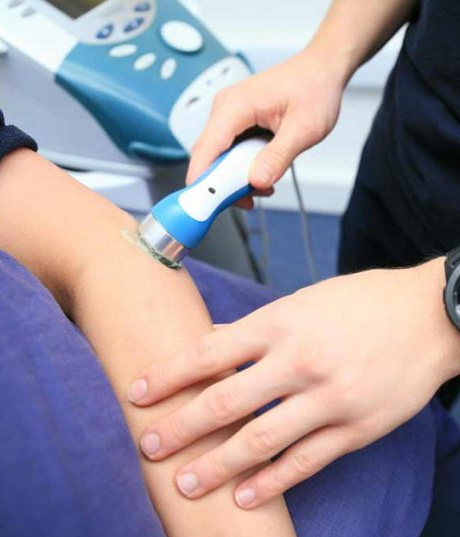
ELECTRO THERAPY
Electrotherapy is a form of medical treatment, which uses small electrical impulses to repair tissue, stimulate muscles and increase sensations and muscle strength.
There are several different forms of electrotherapy; these include ultrasound, interferential therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), laser therapy and muscle stimulation. Ultrasound uses sound waves to speed up the healing process, while interferential therapy and TENS reduce pain by manipulating the nerves which reduces the sensation of pain and produces a tingling feeling. Laser therapy is sometimes used to repair damaged tissue; using lasers means the treatment can be both accurate and intense.
The benefits of electrotherapy are wide-ranging and include a more advanced healing process, a more effective circulatory system and increased muscle tone.




